Civil Engineering and Foundations
(Including Seepage Control)
Summary of uses
Various kinds of bentonite are used in various civil engineering and building foundation works including foundation works for architectural buildings, excavating and jacking works in tunnel or drainpipe works, and development of reservoirs or landscaping ponds. Bentonite is used as a material for a stabilizer to protect the wall surface of the excavated ground or as a material to fill cracks in the ground and increase its waterproof property. Bentonite is often used in combination with water and cement to fill cracks, reinforce the ground, or fix underground cores in civil engineering or construction works.
Use examples
In piling works using drilling mud such as those conducted by the cast-in-place piling method (earthdrill method, reverse method, or boring hole method) or the cast in situ diaphragm wall method, bentonite is used as the chief material for a stabilizer to prevent the pile hole wall from collapsing.
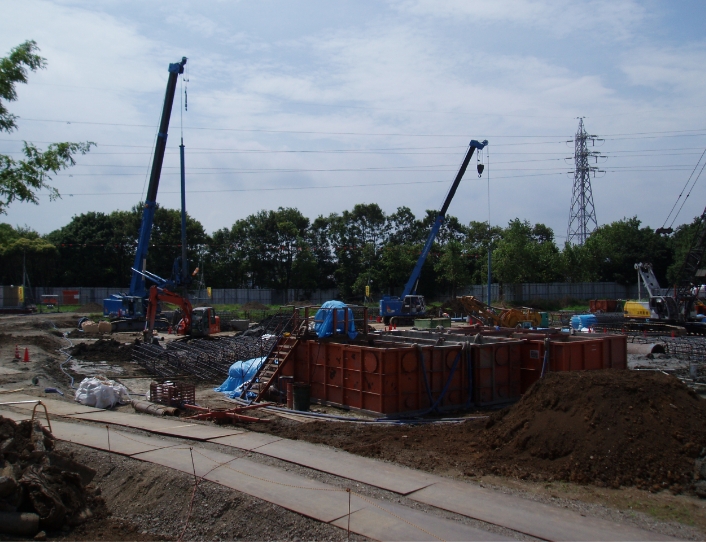
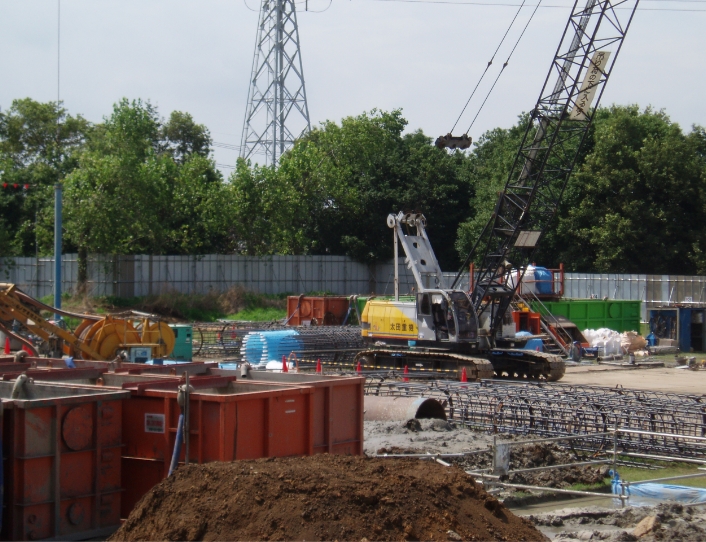
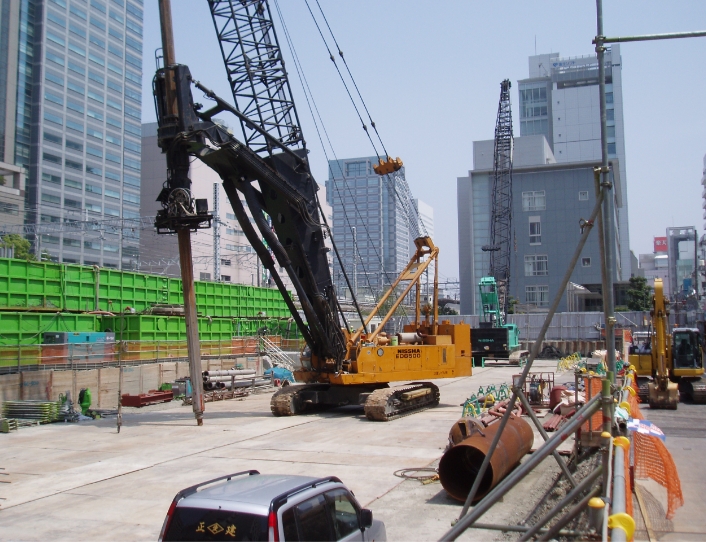



In shielding works or jacking works carried out in tunnel excavation or sewerage pipe installation works, bentonite is used as an important material to effectively carry out excavation and jacking. A cement fluid made by combining bentonite with cement is also used as a back-filling material to fill gaps between tunnels or pipes and the ground and prevent land subsidence.
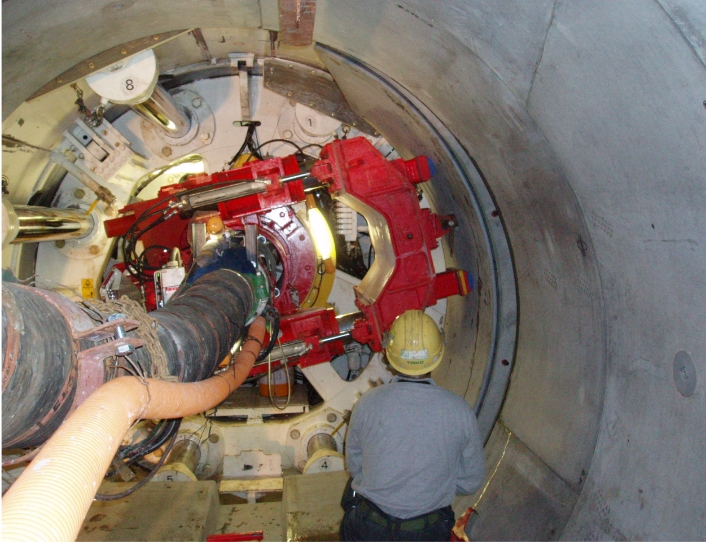
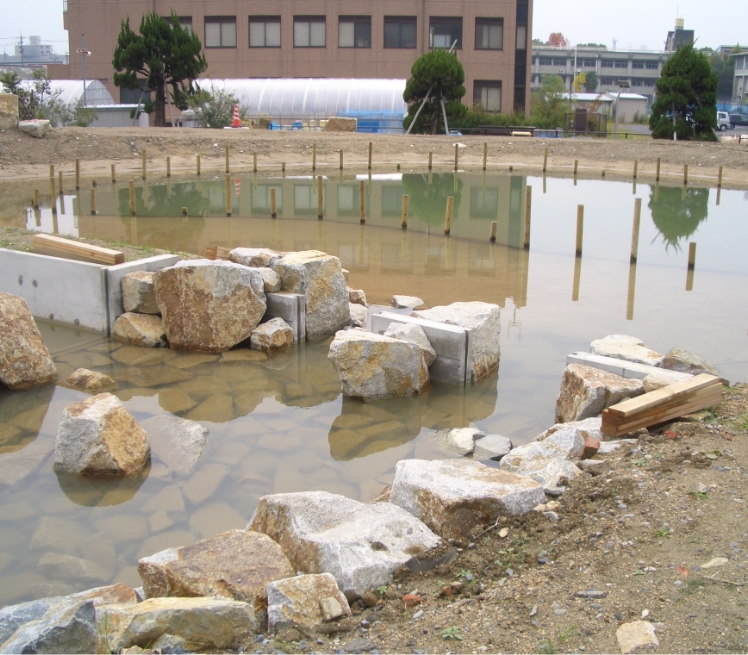


Bentonite is also used in the seepage control work for a reservoir, a landscaping pond, or a biotope to prevent water leakage or infiltration. Bentonite mixed mainly with on-site soil is laid around the pond and in the bottom and compacted by a compaction roller.
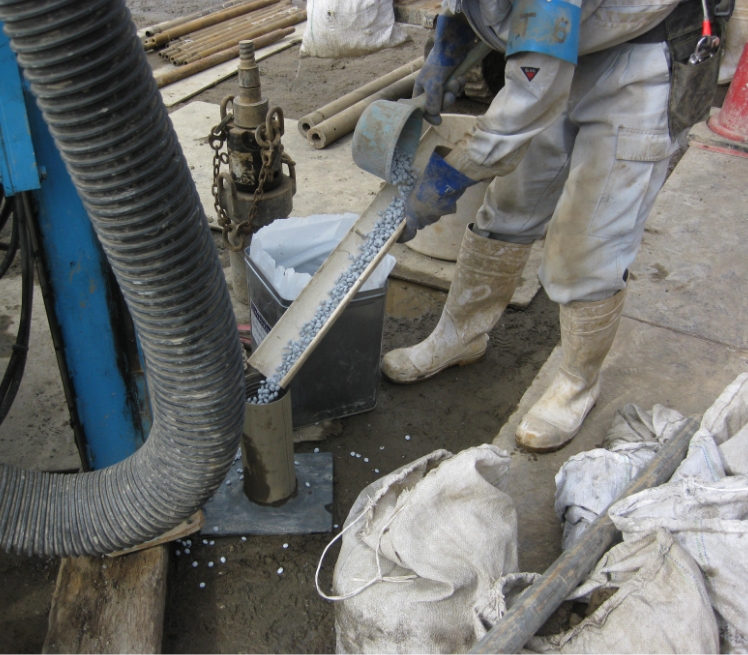

In monitoring wells, exploration wells, and holes made by the deep well method, crushed or granular bentonite is used in the impermeable layer on the bottom. Even in work to form an impermeable layer on the bottom of a several dozen meter deep hole, bentonite granules, which are uniformly shaped and coated with a water infiltration retardant, can be dropped with no concern for bridging to form an impermeable layer as designed just by throwing them into the hole from the ground.
Different construction methods and properties required of bentonite
| Major construction methods | Properties required of bentonite |
|---|---|
| Earth drill method | Viscosity, Wall forming property, Salt resistance |
| Underground continuous wall construction method | Viscosity, Wall forming property, Salt resistance |
| Soil mixing wall method Deep well method | Viscosity, Solid-liquid separation inhibiting property |
| Grout method | Viscosity, Solid-liquid separation inhibiting property |
| Shield method | Viscosity, Solid-liquid separation inhibiting property |
| Pile Construction method | 【Drilling mud】Viscosity(Yield value) 【Cement milk】Viscosity, Solid-liquid separation inhibiting property, Strength |
| Deep well method (Formation of an impermeable layer on the bottom of a hole) |
Waterproof property, Water infiltration retardant property, Apparent specific gravity stability |
Product lineup
Recommended products
| Product name | Earth drill method | Underground continuous wall construction method | Soil mixing wall method Deep well method | Grout method | Shield method | Pile Construction method | Deep well method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KUNIGEL V1 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| KUNIGEL V2 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| KUNIGEL GS | ○ | ||||||
| KUNIGEL VO | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| KUNIGEL MB | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| KUNIGEL CB | ○ | ○ | |||||
| KUNIGEL FS | ○ | ○ | |||||
| EARTH GEL 1 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| EARTH GEL | ○ | ||||||
| OK BENTONITE | ○ |
Other materials
| Product name | Dispersant | Thickener | Lost circulation materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| KS FLOW | ○ | ||
| KUNIPORYMER A | ○ | ||
| KUNIPORYMER H | ○ | ||
| KUNIFORCE NK-G | ○ |
FAQ
What is mesh for distinguishing the quality of bentonite?
Mesh refers to the number of sieve openings per inch. The mesh size of most of our products is 250# (63 μm). In general, a material with a finer mesh size ensures faster dispersion (swelling), but there is little difference in performance due to the mesh size in a completely dispersed state.
What is the slurry used in the process of constructing piles?
Slurry is the muddy water produced by dissolving bentonite, which is the main ingredient, and other organic polymers (polymer, CMC) in fresh water.
It is used to protect and stabilize borehole walls drilled by an earth drill.
Please tell us about the mechanism that protects and stabilizes borehole walls.
The difference in the head pressure and specific gravity of the slurry (muddy water) in mud cake (mud film) formed by muddy water resists the earth pressure and ingress of groundwater.
Mud cake formation process diagram
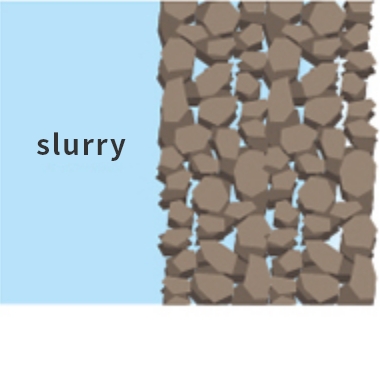
[1] The slurry filling the boreholes penetrates into the borehole wall.
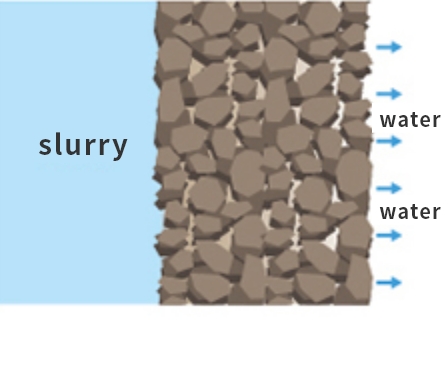
[2] Clay particles enter the small gaps between soil particles.
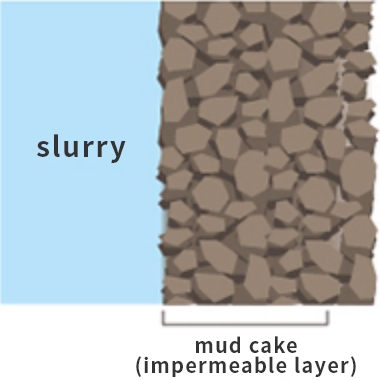
[3] They form mud cake (impermeable layer), which is extremely impermeable to water.
Is bentonite harmful to the environment?
Bentonite itself is not harmful and is used in many fields. It is a natural, inorganic substance and does not decay.
In addition, it is frequently contained, although in small amounts, in ordinary soil.
Furthermore, it is below the standard values in the Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution, the Environmental Quality Standards for Groundwater Pollution, the Judgment Criteria for Landfill Disposal, and other regulations.
Please let us know the importance and points of slurry management.
Needless to say, proper treatment after waiting for slime (cuttings) settling or sedimentation is important. It is important to perform four field slurry tests (specific gravity, viscosity, pH, and sand content) in a timely manner and keep slurry in good condition. However, even if good condition is maintained, various events, such as deterioration, lost circulation, compression, and bacteria growth, occur depending on the situation of the site.
Please contact us for details.
How do you select KUNIGEL GS or KUNIGEL V1 depending on the cement mixing method?
The main difference between them is viscosity; KUNIGEL GS is the highest class, whereas KUNIGEL V1 is a general-purpose product.
In general, a high-class product is used when the condition of the ground is bad, and can also be used for ordinary ground by reducing the amount to be added. Since the amounts of high-class products to be added are small, freight costs and storage places can be reduced. On the other hand, due to the high rise in the viscosity, beware of the formation of clumps during liquid preparation and blockage during pressure feeding.
Please tell me about the sequence of liquid preparation in the cement mixing method.
Before adding cement, mix water and bentonite. Do not mix water and bentonite in a mixer in which cement was mixed. Due to the impact of the Ca ions contained in cement, the amount of bentonite to be added will increase.







